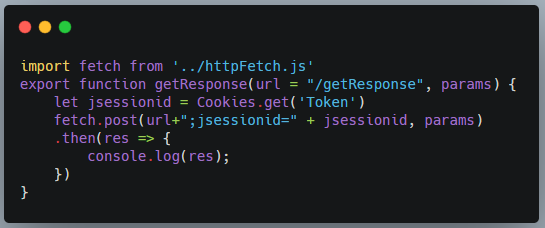
一、Vuex 的功能?能否进行兄弟组件之间的传值?
注意:与 Vue2 匹配的是 Vuex 3,与 Vue3 匹配的是 Vuex 4。
Vuex是一个专为 Vue.js 应用程序开发的状态管理模式。它采用集中式存储管理应用的所有组件的状态,并以相应的规则保证状态以一种可预测的方式发生变化。
主要用于管理 Vue 中的共享状态,可以兄弟组件互相传值。
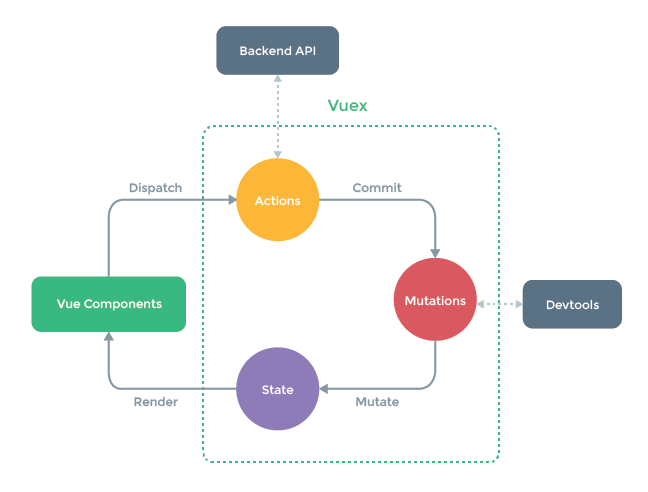
上图的说明:
①Vue Components 是 vue 组件,会触发(dispatch)一些事件或动作(Actions)。
②在 vuex 中,数据是集中管理的,我们不能直接去更改数据,所以会把这个动作(Commit)到 Mutations 中。
③接着 Mutations 就去改变(Mutate)State 中的数据。
④当 State 中的数据改变之后,就会重新渲染(Render)到 Vue Components 中,Vue Components 展示更新后的数据。
Vuex 的核心是 Store(仓库),相当于是一个容器。一个 Store 实例中包含以下属性和方法:
state 定义属性(状态、数据)。
mutations 定义方法(动作):通过提交 mutations 的方式,而非直接改变store.state.count。
通过store.state来获取状态对象,以及通过store.commit方法触发状态变更。
Vuex 和单纯的全局对象有两点不同:
(1)Vuex的状态存储是响应式的。当 Vue 组件从store中读取状态的时候,若store中的状态发生变化,那么相应的组件也会相应地得到高效更新。
(2)不能直接改变store中的状态。改变store中的状态的唯一途径就是显式地提交(commit)mutation。这样使得我们可以方便地跟踪每一个状态的变化,从而让我们能够实现一些工具帮助我们更好地了解我们的应用。
// 创建 store.js 文件
import Vue from 'vue';
import Vuex from 'vuex';
Vue.use(Vuex);
const state = { name: 'Violetks' };
const mutations = {
newName (state, message) {
state.name = message;
}
}
export default new Vuex.Store({ state, mutations })
二、Vuex 的五个核心概念
State、Getters、Mutations、Actions、Modules
三、Vuex 的核心概念之 State
1、单一状态树:Vuex 使用单一状态树,每个应用仅有一个store实例,作为一个唯一数据源。
2、在 Vue 组件中获得 Vuex 状态是通过this.$store.state.xxx,当一个组件需要获取多个状态是可以使用mapState辅助函数。
import { mapState } from "vuex";
computed: {
// 对象形式
...mapState({ sum: "sum", school: "school", subject: "subject" }),
// 数组形式
...mapState(["sum", "school", "subject"]),
}
四、Vuex 的核心概念之 Getters
1、Getters可以认为是store的计算属性,getter的返回值会根据它的依赖被缓存起来,且只有当它的依赖值发生了改变才会被重新计算。
const store = new Vuex.Store({
state: {
todos: [
{ id: 1, text: '...', done: true },
{ id: 2, text: '...', done: false }
]
},
getters: {
// 定义一个 getter
doneTodos: state => {
return state.todos.filter(todo => todo.done)
}
}
})
2、通过属性访问 getter,getter 在通过属性访问时是作为 Vue 的响应式系统的一部分缓存其中的。
store.getters.doneTodos // -> [{ id: 1, text: '...', done: true }]
Getter 也可以接受其他 getter 作为第二个参数:
getters: {
// ...
doneTodosCount: (state, getters) => {
return getters.doneTodos.length
}
}
this.$store.getters.doneTodosCount // -> 1
3、通过方法访问 getter,getter 在通过方法访问时,每次都会去进行调用,而不会缓存结果。
getters: {
// ...
getTodoById: (state) => (id) => {
return state.todos.find(todo => todo.id === id)
}
}
store.getters.getTodoById(2) // -> { id: 2, text: '...', done: false }
4、mapGetters辅助函数,将 store 中的 getter 映射到局部计算属性。
import { mapGetters } from 'vuex';
computed: {
// 对象形式
...mapGetters({ sum: "sum"}),
// 数组形式
...mapGetters(["sum"]),
}
五、Vuex 的核心概念之 Mutations
1、更改Vuex的store中的状态的唯一方法是提交mutation。每个mutation都有一个字符串的事件类型和一个回调函数。
注意:mutation 必须是同步函数。
const store = new Vuex.Store({
state: {
count: 1
},
mutations: {
increment (state, payload) {
state.count += payload.amount;
}
}
})
// 调用 commit 提交到 mutation
this.$store.commit("increment", { amount: 10 });
// 对象风格的提交方式
this.$store.commit({ type: "increment", amount: 10 });
2、使用常量替代 Mutation 事件类型。
// mutation-types.js
export const SOME_MUTATION = "SOME_MUTATION"
// store.js
import Vuex from "vuex";
import { SOME_MUTATION } from "mutation-types";
const store = new Vuex.Store({
state: { ... },
mutations: {
[SOME_MUTATION] (state) { ... }
}
})
3、mapMutations辅助函数,用于生成与mutations对话的方法,即包含$store.commit(xxx)的函数。
import { mapMutations } from "vuex";
methods: {
...mapMutations([
'increment', // 将 `this.increment()` 映射为 `this.$store.commit('increment')`
// `mapMutations` 也支持载荷:
'incrementBy' // 将 `this.incrementBy(amount)` 映射为 `this.$store.commit('incrementBy', amount)`
]),
...mapMutations({
add: 'increment' // 将 `this.add()` 映射为 `this.$store.commit('increment')`
})
}
六、Vuex 的核心概念之 Actions
1、Action类似于mutation,不同在于:Action提交的是mutation,而不是直接变更状态;Action可以包含任意异步操作。
const store = new Vuex.Store({
state: {
count: 0
},
mutations: {
increment (state) {
state.count++;
}
},
actions: {
increment (context) { // context 对象不是 store 实例本身
context.commit("increment");
},
// 执行异步操作:
incrementAsync ({ commit }) {
setTimeout(() => {
commit("increment")
}, 1000)
}
}
})
// 分发 Action
this.$store.dispatch("increment");
// 以载荷形式分发
this.$store.dispatch("incrementAsync", { amount: 10 });
// 以对象形式分发
this.$store.dispatch({ type: "incrementAsync", amount: 10 });
2、mapActions辅助函数,用于生成与actions对话的方法,即包含$store.dispatch(xxx)的函数。
import { mapActions } from "vuex";
methods: {
...mapActions([
'increment', // 将 `this.increment()` 映射为 `this.$store.dispatch('increment')`
// `mapActions` 也支持载荷:
'incrementBy' // 将 `this.incrementBy(amount)` 映射为 `this.$store.dispatch('incrementBy', amount)`
]),
...mapActions({
add: 'increment' // 将 `this.add()` 映射为 `this.$store.dispatch('increment')`
})
}
七、Vuex 的核心概念之 Modules
1、Vuex允许我们将store分割成模块(module)。每个模块拥有自己的state、mutation、action、getter、甚至是嵌套子模块。
// store.js
const countAbout = {
namespaced: true, // 开启命名空间
state: () => ({ ... }),
mutations: { ... },
actions: { ... },
getters: { ... }
}
const personAbout = {
namespaced: true, // 开启命名空间
state: () => ({ ... }),
mutations: { ... },
actions: { ... }
}
const store = new Vuex.Store({
modules: {
countAbout,
personAbout
}
})
2、开启命名空间后,组件中读取state数据。
// 方式一:直接读取
this.$store.state.personAbout.list
// 方式二:借助 mapState 读取
...mapState("countAbout", ["sum", "school", "subject"])
3、开启命名空间后,组件中读取getters数据。
// 方式一:直接读取
this.$store.getters["personAbout/firstPersonName"]
// 方式二:借助 mapGetters 读取
...mapGetters("countAbout", ["sum"])
4、开启命名空间后,组件中调用dispatch。
// 方式一:直接 dispatch
this.$store.dispatch("personAbout/addPerson", person)
// 方式二:借助 mapActions
...mapActions("countAbout", { incrementOdd: "jiaOdd", incrementWait: "jianWait" })
5、开启命名空间后,组件中调用commit。
// 方式一:直接 commit
this.$store.commit("personAbout/ADD_PERSON", person)
// 方式二:借助 mapMutations
...mapMutations("countAbout", { increment: "JIA", decrement: "JIAN" })
八、Axios
Axios 是一个基于 promise 的 HTTP 库,可以用在浏览器和 node.js 中。
九、如何将 Axios 异步请求同步化处理?
//使用 asyns/await
async getHistoryData (data) {
try {
let res = await axios.get('/api/survey/list/', {
params: data
})
this.tableData = res.data.result
this.totalData = res.data.count
} catch (err) {
console.log(err)
alert('请求出错!')
}
}
十、你有封装过 Axios 吗?主要是封装哪方面的?
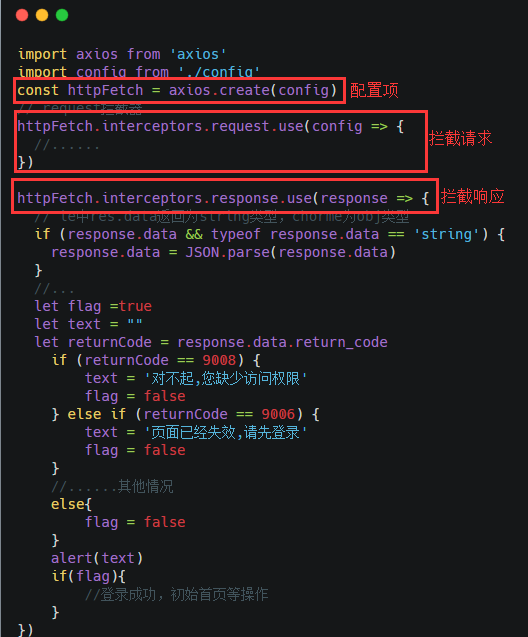
到具体的页面中应用: